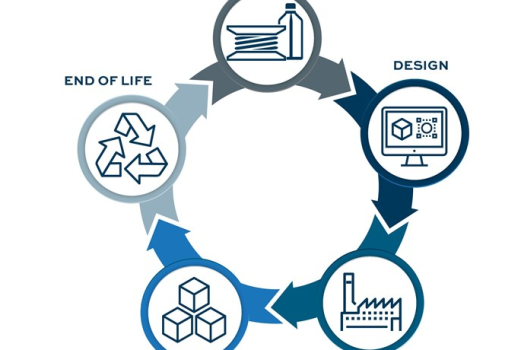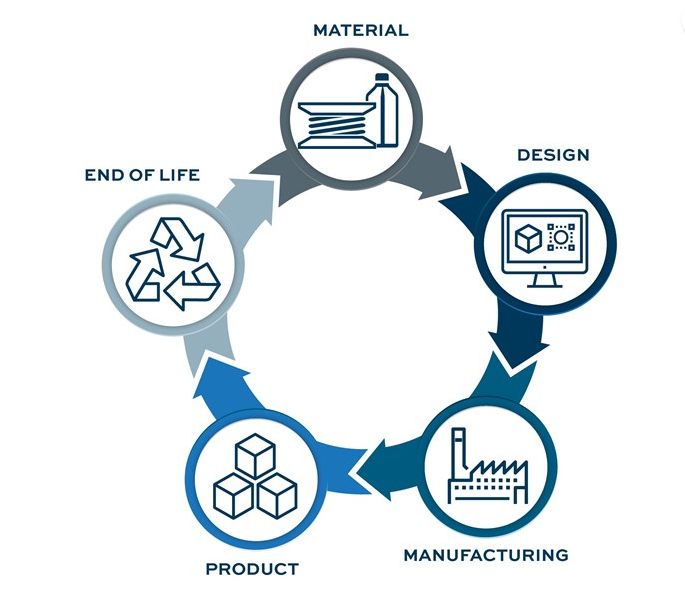
Many people believe that the circular economy is the future of manufacturing. And this economic model is designed to produce goods and services in an environmentally friendly way, by limiting the consumption and waste of resources—such as raw materials, water, and energy. It moves away from the conventional linear economy model, which emphasizes a take-make-consume-throw away model. Instead, the circular economy proposes to transform waste into recycled raw materials for product design or other uses that can literally transform the entire manufacturing process.
The Growth of Circular Economy
The circular economy is not a new concept, but it has gained significant traction in recent years. As the world has become more aware of the environmental and economic challenges of our linear economy, more and more industries and organizations have embraced the principles of the circular economy.
And, the circular economy as a concept is growing significantly among the manufacturing class. This growth is being driven by a variety of factors, including increasing public awareness of environmental issues, the rising cost of raw materials, and government regulations and incentives that promote sustainability.
Many leading manufacturing firms have already adopted circular economy practices in their operations.
How Circular Economy Works
At the heart of the circular economy is the idea of closing the loop. In other words, the aim is to keep resources in use for as long as possible and to extract maximum value from them before eventually recovering and regenerating them. By doing so, it reduces waste and pollution, conserves resources, and ultimately creates a more sustainable future for the product creators.
One of the key ways in which the circular economy can be implemented in manufacturing is through the use of recycled materials. Rather than sourcing virgin materials, manufacturers can use recycled materials to create their products. This not only reduces the demand for raw materials but also helps to keep waste out of landfills.
In addition to using recycled materials, manufacturers can also look to extend the lifespan of their products through repair, refurbishment, and reuse. By designing products to be easily repairable and upgradable, manufacturers can help to reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. Additionally, by encouraging customers to reuse products, manufacturers can reduce the demand for new products and help to conserve resources.
Another key component of the circular economy is the sharing economy. By sharing resources and products, manufacturers can reduce the demand for new products and help to keep existing resources in use for longer. This can be achieved through initiatives such as car-sharing schemes, tool-sharing programs, and co-working spaces.
Here are four benefits of circular economy in detail:
1. Resource Efficiency
The circular economy encourages the efficient use of resources by reusing, repurposing, and recycling materials instead of extracting new raw materials among the manufacturing sector. By extending the life of products, it decreases the amount of waste produced and conserves natural resources.
Plus, it can help address supply chain vulnerabilities for manufacturers by reducing dependence on finite resources that are subject to price fluctuations and geopolitical risks.
2. Reduced Environmental Impact
The circular economy aims to reduce the environmental impact of production and consumption by designing products with the environment in mind, using renewable energy sources, and reducing emissions. By repurposing and recycling materials, the circular economy reduces the amount of waste that ends up in landfills, incinerators, and the environment.
Also, the circular economy can help reduce the carbon footprint of industries emitting large amounts of carbon monoxide and other polluting gases in the atmosphere.
3. Economic Benefits
The circular economy has the potential to create economic opportunities by stimulating innovation, creating new business models, and generating new revenue streams in the manufacturing class. For instance, organizations can benefit from recycling and repurposing materials by reducing production costs, increasing efficiency, and improving their environmental credentials.
Ultimately, the circular economy represents a shift away from the linear economy model in the manufacturing sector and towards a more sustainable future. By focusing on the principles of reduce, reuse, and recycle, manufacturers can help to create a more circular economy and a more sustainable world for future generations.